To accompany our example of a multi-tiered (spend more, save more) promotion set up in Magento, we’ve created this brief description of the Shopping Cart Price Rules fields and their functions. When setting up promotions, or making any changes for that matter, be sure to test thoroughly before you leave it to run on its own. If you don’t have a test site to do so, try creating first creating promotions that are not very drastic and setting them Active during hours of the day when you’re least likely to have site traffic.
To accompany our example of a multi-tiered (spend more, save more) promotion set up in Magento, we’ve created this brief description of the Shopping Cart Price Rules fields and their functions. When setting up promotions, or making any changes for that matter, be sure to test thoroughly before you leave it to run on its own. If you don’t have a test site to do so, try creating first creating promotions that are not very drastic and setting them Active during hours of the day when you’re least likely to have site traffic.
Fields Overview:
Tab: Rule Information
This tab contains general rules including timeline, groups that the promotion will apply to, internal description, and other broad rules.
It includes the following fields (mandatory magento fields always marked with asterisk):
Rule Name: This is for internal use only (i.e. 30% off Labor Day Sale). Rule Name will appear on your Promotions list so include enough detail to distinguish promotions as the list number increases.
Description: Not a mandatory field, but this is your opportunity to spell out the rules of the promotion in plain English for future reference for yourself or others.
Status: Active or Inactive, determines whether your promotion is applied on your site.
Customer Groups: If you have different customer groups and access set up on your site, this field allows you to limit a promotion to only specific groups (e.g. Members Only Sale).
Coupon: Magento offers you the option to choose No Coupon or Specific Coupon
- No Coupon: Select this option to apply the promotion to all eligible site users (e.g. general sales)
- Specific Coupon: Allows you to enter the coupon code of your choice. Use this option for targeted promotions, reachout, or any discount you’d like to provide to a limited number of customers.
- If you choose Specific Coupon option, you’ll have the further option to Use Auto Generation. If selected, Magento will auto generate codes which you can then manage and distribute.
Uses Per Coupon- Depending on your business and the scope of your promotion, use this field to limit uses per your wishes or set to an arbitrarily high number to–in effect–have no limit until the promotion expires or is manually ended
Uses Per Customer: Again, this very much depends on the manner of the promotion you are running. Set according to your wishes.
- Note: This will be tracked according to customer accounts. If you are trying to limit a coupon to say, only one use, do not use this field. Not only can the coupon be shared but multiple accounts can be created by customers.
From Date: Allows you to specify start date of your promotion. Note that whether a promotion is Active or not is independent of this field. If you plan to set a future start date, set your promotion to Active AND enter a From Date.
To Date: Allows you to specify the end date of your promotion (ending a minute before midnight on the date entered).
Priority: This field is important when running multiple promotions, and essential to creating Multi-Tiered spending promotions (i.e. spend X, get Y% off; spend 2X, get 2Y% off).
The lower the number entered here the higher the precedence/priority in the application of your promotion.
In our three-tiered example we choose an arbitrarily high number (low priority) to begin with and assign decreasing numbers to each tier
- Spend 100 get 10% off: Priority- 33
- Spend 200 get 20% off: Priority- 32
- Spend 300 get 30% off: Priority- 31
The Priority number you assign promotions will depend on the size and nature of your business and promotions. As a general rule, the less your promotion is limited in scope, the lower number you can assign to it.
See related field Stop Further Rules Processing
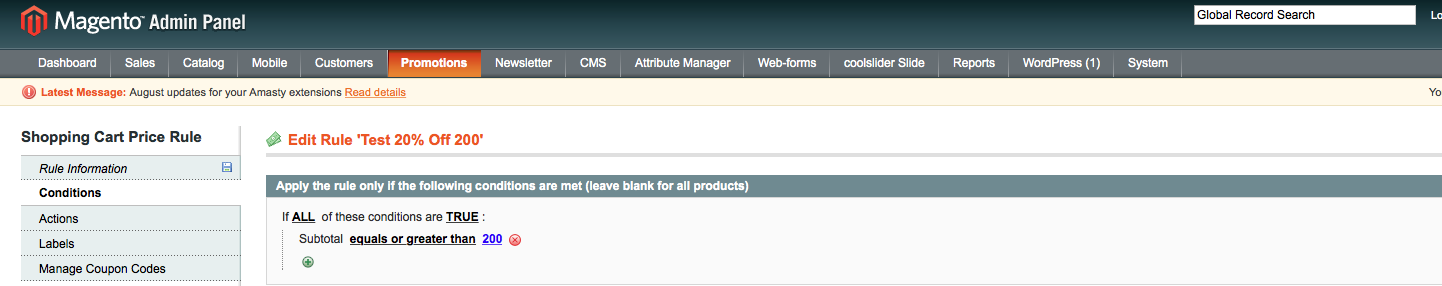
Tab: Conditions
This tab contains the essential rules or criteria that must be met in order for your promotion to apply.
The rules are fairly easy to set up, and allow for a virtually endless list of conditions.
Generally, by selecting If All conditions Are True you can endlessly narrow down the promotion by product # /products / product attributes / total cost / and so on.
By selecting If Any Conditions are True (or False) you can cast a wider net, allowing you to choose multiple products or price ranges.
In our example, we have a very simple rule set up for the 2nd rule in our three-tiered Spend X, Save X example: the promotion will apply if the customer’s subtotal is equal to or greater than $200.
Tab: Actions
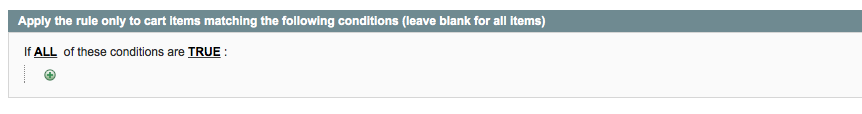
In the Actions tab, you are able to define what happens IF the rules in the Conditions tab are met. It further contains a section that allows you to apply extra conditions to items in the cart, narrowing to specific categories, prices, and more as needed. In our example, we leave this section blank as we have no need to further narrow the application of the promotion.
Section- Apply: Has four, relatively self-explanatory options for what kind of discount is applied in your promotion:
- Percentage of Price Discount: Allows you to enter a percentage that will be taken off of the subtotal in the Discount Amount field below. In our example, we use this field to create 20% Off
- Fixed Amount Discount: Allows you to enter a fixed monetary amount (in the next field) to be taken off of products that you define in the second section of this page. If left blank, it will apply to all products that have met the criteria in the Conditions tab.
- Fixed Amount Discount for the Whole Cart: Allows you to enter a fixed monetary amount to be taken off of products that you define in the second section of this page. As stated, this rule applies to the entire cart.
- Buy X get Y free (discount amount is Y): Allows you to set up a rule specifying number of item(s) X purchased in order to receive number of items(s) Y free.
Discount Amount: This field is the percentage or fixed amount discounted depending on the Apply action you selected in the step before. In our example, this is where we specify 20 for 20% off purchases over $200.
Maximum Quantity Discount is Applied to: Allows you to limit the number of products that can are discounted if stock or margins are low.
Discount Qty Step (Buy X): This section is where you specify the amount of product X purchased in order to receive product Y if you’ve selected the Buy X get Y free (discount amount is Y) Apply action.
Apply to Shipping Amount: Determines whether the price rule, if a percentage or a fixed number that exceeds subtotal will apply to shipping costs.
Free Shipping: Simple yes/no option to offer free shipping with your promotion (or as your promotion).
Stop Further Rules Processing: This is an important field when running simultaneous or complimentary promotions. Selecting Yes prevents any further promotions from applying on top of the one you’re creating. When this is the case, it is the Priority numbers assigned to each promotion that will determine which one ultimately applies.
In our multi-tiered example, we set this to Yes. Otherwise, using three separate promotions for one “Buy 100 get 10%, Buy 200 get 20%, Buy 300 get 30%,” each rule would apply to a purchase of over $300 dollars, effectively becoming %50 Off.
The second section under this tab is “Apply the rule only to cart items matching the following conditions (leave blank for all items)” – This is where you you specify what items the promotion will actually apply to, as opposed to the Conditions tab, which specifies which items (amounts, etc.) activate the promotion in the first place. It has essentially the same logic rules available as the Conditions tab, and can be used exclusively or in combination with Conditions depending on the specific promotion you would like to create.
Tab: Labels
This section is where you give your promotion the title that you would like site users to see. Whether and where it shows up will depend on the way your site is constructed, but will usually appear on the checkout page.
Tab: Manage Coupon Codes
This section is fairly self-explanatory and, of course, only applies if you’re using a promotion that requires a coupon. It is primarily for coupons that you want to closely manage. E.G. a small number of unique coupons to provide to a few exclusive reviewer, in most cases it’s easier and more manageable to enter a single coupon code under the Rule Information tab.
Coupon Quantity: Determines how many coupons will be created.
Code Length: Length of the coupon to be generated.
Code Format: Alphanumeric, Alphabetical, or Numeric.
Code Prefix / Code Suffix: Manually add a set prefix or suffix for organization and management of multiple unique codes.
Dash every X characters: Insert a dash in order to make your coupons uniform with another system or extra unique